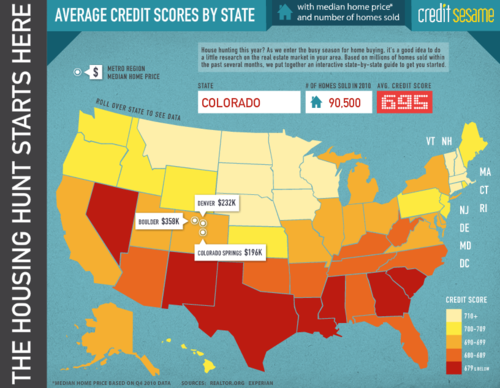
(click on the map to go to the interactive graphic)
Do you know what your credit score is? Maybe you should try surviving the credit storm before you start buying houses…
(Via Column Five for Credit Sesame)

(click on the map to go to the interactive graphic)
Do you know what your credit score is? Maybe you should try surviving the credit storm before you start buying houses…
(Via Column Five for Credit Sesame)

(photo credit: bredgur)
It’s not often that the Wall Street Journal writes for readers under 40, but they just published a really good article with financial advice for the pre-college population. Now, we’re not trying to get all parenty on you, but as pseudo-grownups we can assure you that a little planning goes a long way.* (And it really doesn’t take that much time out of your schedule.) Here are some of the points writer Zac Bissonnette makes:
(TILE Fun Fact: A small amount of debt can actually help you, by rounding out your credit history and boosting your credit score. But ONLY if you use it responsibly – that means pay it off, and never miss a due date.)
The most important question you need to ask yourself is this: What is this college degree really going to cost me, in terms of my dreams? Maybe you’d like to travel the world after graduation, or take an entry-level job in the nonprofit sector, or buy your first house before you’re thirty. Massive debt can really screw up your plans, so plan accordingly.
* For example, if you chose to invest $1,000 at age 18 and earned a paltry 3% return, you could have $3,500 waiting for you when you’re 60. (And by the time you’re 60, 60 will be the new 30.) All that with absolutely no effort. Well, you do have to take an hour to invest that $1,000 when you’re 18. See what we mean about planning?
Play with your own numbers to see what a little investment today can earn you: Compound Interest Calculator

(credit: JASON ANFINSEN)
Going to Bonnaroo this year? Prepare to wear your credit card on your sleeve. Er, wrist. Concert producers have switched from a paper-based to a microchip-based ticketing system, which means you’ll be wearing your right to be there in a little plastic bracelet on your wrist.
But wait, there’s more! Concertgoers can also choose to embed their credit card information in their bracelets, so they’ll be able to pay for stuff without searching for their wallets. (We all know how much of a hassle that is, right?)
You’ve got to love how easy it’s becoming to spend money. Okay, maybe it’s not such a good thing for our budgets (or our souls) here in the U.S., but think about the implications for people who live in countries with developing economies… Technology like this could eliminate a lot of hurdles to economic participation – kind of like how the invention of the cell phone ended up democratizing long-distance communication in Africa. (In 2005, 1 in 11 Africans had a mobile plan; only 1 in 33 had a land line.)
Synergy, besides being one of those infamous “corporate buzzwords,” is the combination of at least two things (for example companies or organizations) to produce a financial benefit that’s greater than the sum of its parts.
For example, by purchasing one company, another company might be able to generate more revenue than both companies would have been able to generate if they kept operating separately. (Think Graham Crackers Inc. and Melty Marshmallows LLC being acquired by Hershey’s.)
OPEC stands for “Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Counties.” It is a cartel made up of 12 countries: Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela.
These countries produce much of the oil that the rest of the world buys, so they’ve banded together to ensure that everyone receives a fair price for their oil. The oil ministers of the member countries meet regularly in Vienna to discuss oil prices and production.
A Plutonomy is an economy that is driven and controlled by an extremely wealthy minority. The word was coined in 2005 by an analyst at Citigroup. According to the laws of Plutonomics, the rich – because they spend a lot of money – make up such a large proportion of national spending that they mess with national spending statistics.
For example, if you asked everyone in the country how much they spend on designer clothes each year, and averaged that number, you would get an inaccurate picture of how well America is dressing. Why? Because one person spending $10,000 a year on couture while 9 other people spend $0 still makes it look like everyone is dropping $1,000 on their “collection” every year.
Sexism is discrimination against a person or persons on the basis of gender. Like racism, it can occur explicitly (violence against women, demeaning comments), unconsciously (unintentionally excluding female coworkers from after-work dinners and casual meetings), or institutionally.
An annuity is a kind of tax-deferred retirement plan, but it’s usually operated through an insurance company. You pay the insurance company a certain amount of money, and in return that company promises to pay you back with interest over a period of time. An annuity is a simple way to save money for retirement without paying taxes on it right away.
You can pay into your annuity all at once (“lump sum”) or in a series of payments. Depending on your contract, an annuity might start paying you back right away or start at a later date – such as when you plan to retire.
A minimum wage is the absolute minimum amount of money that someone can be paid for a specified job. It was created to ensure that no one is unfairly compensated for their work. As of July 2009, the federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour.
In the U.S., the minimum wage is regulated by the federal agency called the Department of Labor, but states have the flexibility to set their own higher (or in special cases, lower) minimum wage. There are also exceptions to who must receive the minimum wage. Waiters and other workers who regularly receive tips have a much lower minimum wage ($2.13/ hour). And sometimes employers can pay workers who are under 20 only $4.25 per hour for their first 90 days on the job.
Frank Murtha from MarketPsych returns with some insight about how that annoying habit from high school follows most people into their grown-up financial lives. If you’ve been jumping off bridges after your friends up until now, maybe this will convince you to stop:
>> TILE brings you exclusive opinions, explanations, and interviews from experts in every industry. Have a burning question or an expert you’d like to see interviewed? Just Ask TILE!